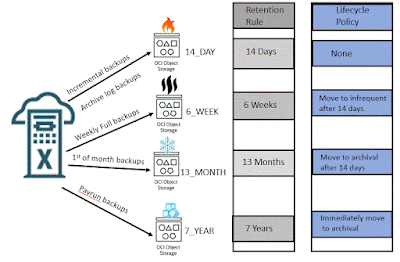
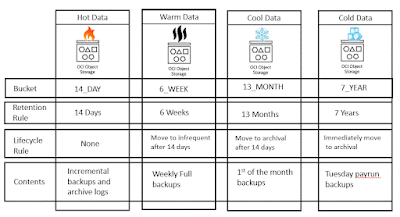
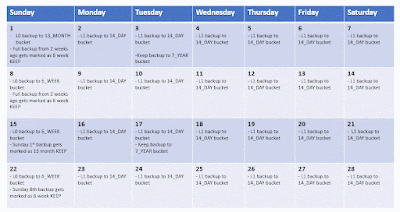
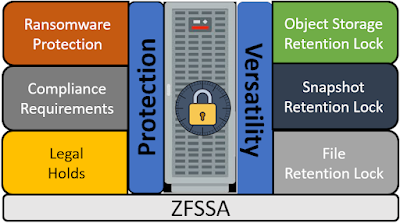
The latest release of ZFSSA software OS8.8.45 includes file retention locking, joining object retention lock and snapshot retention lock providing both versatility and protection of your data.
3 types of retention lock
Legal Hold
You might need to preserve certain business data in response to potential or on-going lawsuits. A legal hold does not have a defined retention period and remains in effect until removed. Once the legal hold is removed, all protected data is immediately eligible for deletion unless other retention rules still apply.
NOTE: Both Data Governance and Regulatory Compliance can be use to protect from any kind of cyber/ransomware attack.
Data Governance
Data Governance locks data sets (snapshot, object or file) for a period of time protecting the data from deletion. You might need to protect certain data sets as a part of internal business process requirements or protect data sets as part of your cyber protection strategy. Data Governance allows for adjustments in the retention strategy from privileged users.
Regulatory Compliance
Your industry might require you to retain a certain class of data for a defined length of time. Your data retention regulations might also require that you lock the retention settings. Regulatory compliance only allows you to increase the retention time if at all. Regulatory Compliance is the most restrictive locking strategy and often does not allow anyone, even an administrator, to make changes affecting retention.
3 implementations of retention lock
Object storage
Object storage retention is managed through the OCI client tool and Object retention is enforced through the API. Current retention settings are applied to all objects when they are accessed. Adding a rule immediately takes affect for all objects.
Administration of retention rules can be managed through the use of RSA certificates. It is recommended to create a separation of duties between a security administrator, and the object owner.
Retention on object storage is implemented in the following way based on the retention lock type.
Legal hold
Legal holds are implemented by placing an indefinite retention rule on a bucket. Creating this rule ensures that all objects within the bucket can not be deleted, and cannot be changed. Only new objects can be stored.
Data Governance
Data Governance is implemented by placing a time bound retention rule on a bucket. The rule sets a lock on all objects for a set length of time. The rule can be later deleted. For cyber protection it is recommended to implement this with a separation of duties.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory Compliance is implemented by placing a locked time bound retention rule on a bucket with a grace period. When a locked time bound retention rule is created it immediately takes effect, but there is a grace period of at least 14 days before the rule becomes permanent which allows you to test the rule. Once the grace period expires (defined by a specific date and time) the rule cannot be deleted even by an administrator.
Snapshots
Snapshot locking is managed the BUI, or CLI. Individual snapshots can be locked, and scheduled snapshots can be created and automatically locked. Permission for controlling snapshot locking can be assigned to ZFSSA users allowing you to create a separation of duties. Shares or projects cannot be removed if they contained locked snapshots.
Retention on snapshots is implemented in the following way based on the retention lock type.
Legal hold
Because snapshots only affect data that is on the project/share when the snapshot is taken, it is not possible to lock all new data as it is written. Manual snapshots can be used to provide a mechanism to capture the content of a share as of the current time. This could suffice for a Legal Hold. A manual snapshot can be created with a "retention lock" of UNLOCKED creating a snapshot that cannot be removed. The only way to remove the snapshot is by changing the "retention lock" to OFF, unlocking it for deletion. This creates a hold on the current data for an indefinite period of time. Permissions for releasing the hold on a the snapshot can be assigned to specific individual account allowing for a separation of duties.
Data Governance
Data governance of snapshots is handled through the use of scheduled locked snapshots and enabling the retention policy for scheduled snapshots. A LOCKED schedule is created with both a retention, and "keep at most" setting. This allows you to manage snapshots for a locked number of snapshots, while automatically cleaning up snapshots that are past the retention number. The snapshots within the retention number can not be unlocked, and the schedule can not be removed as long as there is data contained in the snapshot.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance of snapshots is handled through the same method as Data Governance. Snapshots cannot be be removed when they are locked, and the schedule remains locked.
File Retention
File retention is set at the share or project level and controls updating and deletion of all data contained on the share/project. A default file retention length is set and all new files will inherit the default setting in effect when the file is created. It is also possible to manually set the retention on a file increasing the default setting inherited by the file.
Legal Hold
Legal Holds on files is implemented by manually increasing the retention on individual files. Because a Legal Hold may be required for an indefinitely period of time, it is recommended to periodically extend the retention on files needed within the legal hold. This allows the files retention to expire once the need the for the Legal Hold has passed.
Data Governance
Data governance is implemented by creating a NEW project and share with a file retention policy of privileged. Privileged mode allows you to create a default retention setting for all new files, and change that setting (longer or shorter) going forward. Files created inherit the retention setting in effect when they are created. Retention can also be adjusted manually to be longer by changing the unlock timestamp. Projects/shares cannot be deleted as long as they have locked files remaining on them.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is implemented by creating a NEW project and share with a file retention policy of mandatory (no override). Mandatory mode does not allow you to decrease the default file retention. Retention can also be adjusted manually to be longer by changing the unlock timestamp. Regulatory Compliance uses the same mechanisms as Data Governance but is much more restrictive. The project/share cannot be removed when locked files exist, and the storage pool cannot be removed when locked files exist within the pool. This mode also requires an NTP server be utilized, and root is locked out of any remote access.
The best way to explore these new features is by using the ZFSSA image in OCI to test different scenarios.